SingSong: Google AI Researchers Find a Way to Generate Music to Accompany Input Vocals

In Brief
The new system called SingSong uses a deep learning model to generate music that is more in sync with singing than existing systems.
The researchers say that the system could be used to create karaoke tracks for professional singers or to help amateur singers find accompaniment that matches their voices.
Researchers at Google have found a way to use artificial intelligence to generate music that is compatible with singing. The new system, called SingSong, uses a deep learning model to generate accompaniment that is more in sync with singing than other existing systems. The researchers say that the system could be used to create karaoke tracks for professional singers or to help amateur singers find accompaniment that better fits their voices.

SingSong is a system developed by Google that creates instrumental music to accompany input vocals. It may provide both musicians and non-musicians with a simple new approach to making music that features their own voices. Developers build on recent advancements in musical source separation and audio production to achieve this. Developers specifically use a cutting-edge source separation method to build aligned vocal and instrumental source pairs from a massive corpus of music recordings. Then, developers modify AudioLM, a cutting-edge method for unconditional audio production, so that it may be trained on source-separated (vocal, instrumental) pairs for conditional “audio-to-audio” generation tasks.
| Recommended post: Top 5 AI Music&Audio Generators to Create Royalty Free Tracks |
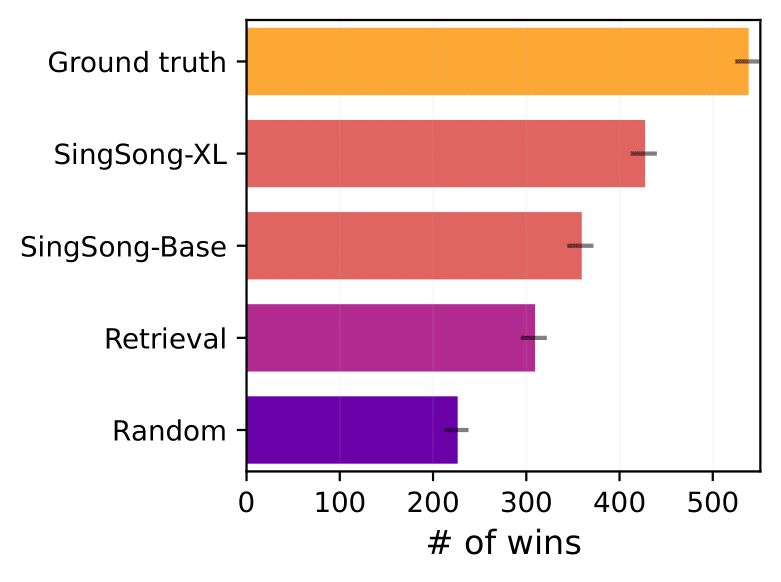
AI researchers investigate different featurization of vocal inputs, the best of which enhances quantitative performance on isolated vocals by 53% compared to the default AudioLM featurization, in order to improve the system’s generalization from source-separated training data (where the vocals contain artifacts of the instrumental) to isolated vocals developers might expect from users. Listeners exhibited a substantial preference for instrumentals produced by SingSong over those from a strong retrieval baseline in a pairwise comparison with the same voice inputs.
The new system, by contrast, uses a deep learning model that has been trained on a large dataset of music. This allows the system to generate accompaniment that is in sync with the singer’s voice and timing.
For the study, listeners are given two 10-second vocal-instrumental mashups in which the voices (taken from the MUSDB18-test) are the same while the instrumentals differ and come from various sources (ground truth, google models, or baselines). The question asks listeners to choose which of the two combinations they feel the instrumental backings fit the vocals more musically.
| Recommended post: Top 7 AI voice generators and voice cloning for text-to-speech |
SingSong’s Fresh Examples
By using a series of deep neural networks and generative models, developers are able to produce harmonic accompaniments with no latency for longer segments.
The MUSDB18 dataset’s professional voices were used in the preceding examples. We are also intrigued by SingSong’s ability to support and enable anyone to create music with their voice. Here, we examine this using vocal samples from the Vocadito dataset, which includes recordings of amateur vocalists made on consumer electronics.
The system is still in the early stages of development. While the researchers say it will need to be improved before it can be used commercially, they believe that it has the potential to revolutionize the karaoke industry and help amateur singers find accompaniment that works well for them.
Read more related articles:
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.
More articles

Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.






















































