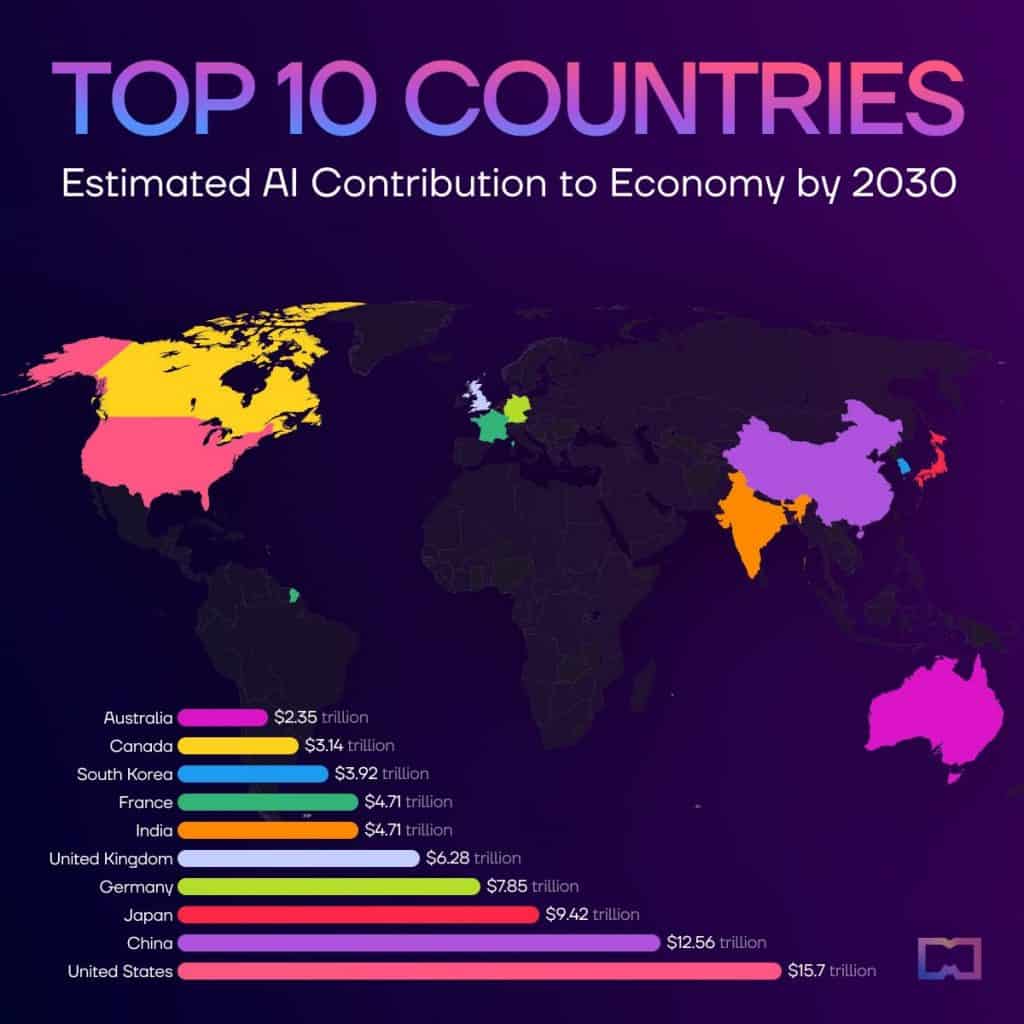
Ranked: Top 10 Countries by Estimated AI Contribution to Economy by 2030


In Brief
AI embodies the forthcoming paradigm shift in technology, poised to revolutionize global economies comprehensively.
As AI capabilities progress, nations are engaged in a fervent pursuit to secure leadership and competitive advantages in the development and deployment of these cutting-edge technologies.
Within this discourse, we endeavor to enumerate the top 10 countries prognosticated to derive maximal economic benefits from the impending acceleration of AI throughout the next decade.
AI stands at the cusp of a transformative era, poised to reshape virtually every sector and ignite economic shifts worldwide during the forthcoming decade. Certain nations are strategically positioned to maximize the potential of AI and reap its economic benefits.
1. The United States
The United States boasts a preeminent status as the global epicenter for AI research and development. Anchored by tech behemoths such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Facebook, and IBM, the U.S. commands over half of the global investments in AI startups.
It serves as an alluring magnet for the most proficient AI talents. Leading metropolitan areas like San Francisco, New York, Boston, and Seattle have blossomed into epicenters for top-tier AI researchers and engineers.
PwC’s prognostication indicates that AI will infuse a staggering $15.7 trillion into the U.S. economy by 2030. Prominent sectors poised to profit include healthcare, automotive, finance, agriculture, retail, and cybersecurity. The U.S. Department of Defense occupies a central role in financing AI research, particularly in national security matters.
2. China
China has set forth ambitions to ascend to the zenith of the AI landscape by 2030. Enshrined within the country’s “Next Generation AI Development Plan” is the aspiration for China to emerge as a pivotal global hub for AI innovation. A McKinsey report posits that the integration of AI could catapult China’s GDP by a notable 26% by 2030.
China’s tech titans, including Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent, have unleashed substantial resources towards AI research, with a dedicated focus on domains such as smart urbanization, finance, autonomous mobility, and healthcare. Additionally, China unfurls considerable governmental backing for the advancement of AI, proffering incentives and subsidies for nascent startups.
3. Japan
While trailing the U.S. and China in the AI race, Japan has embarked on a concerted journey to attain eminence in AI, with over 250 enterprises deeply immersed in AI-related research and development. The Japanese government has bestowed paramount importance upon nurturing its AI sector, channeling substantial investments, and fostering the inception of startups.
Japan unveiled its “AI Technology Strategy” in 2017, articulating a comprehensive blueprint for infusing AI across myriad domains, encompassing manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, and cybersecurity.
Japan’s unique strengths, including cutting-edge robotics, an expansive reservoir of engineering virtuosity, and a cultural penchant for precision and automation, serve as the bedrock for AI innovation. The hosting of the 2020 Olympics in Tokyo served as a catalyst for widespread AI integration into the nation’s infrastructure.
Projections by analysts suggest that AI could infuse an impressive $170 billion into Japan’s economy by 2030. Prominent Japanese conglomerates venturing into AI include Toyota, Fujitsu, NEC, Hitachi, and Mitsubishi.
4. The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom is solidifying its stature as a formidable hub for AI research and adoption, standing alongside the U.S. and China. Accenture posits that AI could yield an astounding $814 billion for the UK economy by 2035. In 2019, the British government unveiled its AI Sector Deal policy, outlining a comprehensive framework to bolster AI research and commercialization.
Academic meccas such as Oxford, Cambridge, Edinburgh, and London have cultivated an ecosystem that magnetizes prodigious talents specializing in machine learning and neural networks.
The UK currently incubates over 600 startups dedicated to AI. Noteworthy applications encompass intelligent algorithms fortifying cybersecurity, predictive analytics reshaping finance, and AI-driven virtual assistants enhancing customer service.
Prominent multinationals with a British footprint, including Rolls Royce, HSBC, Barclays, and British Telecom, are steering AI endeavors. Anchored by robust infrastructure and incentives that catalyze innovation, the UK is poised to foster further AI breakthroughs in this decade.
5. Canada
Canada has recently surged forth as a global pacesetter in AI research. Home to pioneering luminaries such as Geoffrey Hinton and Yoshua Bengio, Canada stands as the birthplace of some of the most extensively cited research papers in AI. The Canadian government has embarked on an endeavor to capitalize on this momentum, unveiling its “AI Strategy for Canada” in 2017, a concerted effort to stimulate research and commercialization.
AI hubs in Montreal, Toronto, Edmonton, and Vancouver have emerged as magnetic beacons, drawing top-tier talent from across the globe. A paramount strength of Canada lies in its adeptness at enticing and retaining AI luminaries from the international diaspora, underpinned by quality of life and immigration enticements designed to ensnare skilled tech artisans.
According to Accenture, the infusion of AI could inflate Canada’s GDP by a remarkable $150 billion by 2035. Thriving sectors embracing AI encompass healthcare, natural resources, retail, and financial services. With preeminent research institutions and an environment conducive to commerce, Canada shall persist as a vanguard in AI.
6. Germany
Germany bequeaths a solid foundation in engineering and automation, ideal prerequisites for fostering AI adoption. 2018 the German government unveiled its national AI strategy, delineating a roadmap to construct a commanding AI ecosystem. Germany offers exceptional research establishments like the DFKI research center and an extensive talent pool. Notable conglomerates engaged in AI initiatives span engineering, automotive, chemicals, manufacturing, and electronics.
Germany boasts niche proficiencies in robotics and industrial applications of AI. The Fraunhofer Society is one of Europe’s most prominent research institutions specializing in applying AI solutions to manufacturing and logistics.
The nation’s robust engineering and automation culture lends itself splendidly to exploring AI’s utility across multifarious sectors, including supply chain management and intelligent manufacturing. Analysts envisage AI contributing over $200 billion to Germany’s GDP within the next 15 years.
7. France
France has declared its intent to vie globally in AI research and assimilation. In 2018, French President Emmanuel Macron unveiled an ambitious national AI plan, allocating $1.6 billion for research. This blueprint pivots around reinforcing France’s cohort of AI researchers, the catalyzation of startups, and the inculcation of ethical considerations into AI design.
France already proudly boasts over 500 AI startups, with Paris emerging as a burgeoning epicenter for AI innovation.
France wields a pantheon of strengths in AI, including distinguished mathematicians, an open data movement, and a government that diligently designs its AI trajectory. France takes pride in globally acclaimed AI research institutes such as INRIA and the CNRS.
Major French conglomerates actively embracing AI solutions encompass Renault, Airbus, Atos, Suez, and Total. AI applications in finance, medicine, and energy proffer significant promise within the French milieu. If governmental initiatives gain traction, France possesses the potential to nurture a robust AI ecosystem throughout the forthcoming decade.
8. Israel
Israel has become a juggernaut for emerging technologies, AI being no exception. With a startup density unparalleled anywhere else in the world, Israel has amassed over 1,000 companies exclusively dedicated to AI and machine learning, having secured over $2 billion in funding since 2015. AI applications stand particularly promising within domains such as cybersecurity, agriculture, finance, and autonomous mobility.
Israel basks in the splendor of innovation hubs such as Silicon Wadi and a workforce distinguished by its erudition and tech-savvy acumen. The Israel Innovation Authority extends generous grants to expedite R&D undertakings. Multinational giants like Intel, Microsoft, IBM, and Samsung have entrenched formidable R&D bastions within Israel, exclusively devoted to AI innovation.
Pioneering AI players hailing from Israel encompass Mobileye, OrCam, and Voyager Labs. Propelled by its “startup nation” repute, Israel occupies a vantage point to catalyze AI innovations in the upcoming decade.
9. South Korea
South Korea charts a course to fortify its high-tech economy by propelling its AI capabilities to the forefront. The nation allocated $2 billion in 2022 to establish an AI R&D infrastructure. South Korea has advanced digital infrastructure and boasts one of the highest densities of robots globally. Prominent players like Samsung, Hyundai, and SK Telecom spearhead multifarious AI applications.
To consumer electronics and telecommunications, South Korea aspires to embed AI across domains such as manufacturing, finance, security, and public services. A distinctive aspect of its ambition lies in the aspiration to construct “smart cities” meticulously designed to harness the potential of AI and big data.
10. Singapore
Singapore, celebrated for its tech-savvy culture and business-friendly ambiance, aims to ascend as a beacon of AI development within the Southeast Asian sphere. The government’s “AI Singapore” initiative extends funding and infrastructure to groom Singapore as a hub for AI research and commercialization. Singapore harbors specific proficiencies in sectors such as fintech, communications, logistics, and transportation, arenas poised to reap the rewards of AI integration lucratively.
Boasting a highly educated, multilingual workforce, Singapore magnetizes talents and entrepreneurs from the vast tech landscape. The city-state offers tangible urban settings, ideal for piloting AI solutions at scale. Noteworthy multinational juggernauts, including Microsoft, Grab, and Alibaba, have elected to expand their Asian AI operations, with Singapore as their strategic anchor.
Pros of Using AI in Economies
Using AI in a country’s economy can bring many good things:
- Getting more done with less effort – AI can do tasks on its own, which means less work for people and more time for important things. That makes the economy more productive.
- Becoming more competitive – Companies using AI can do things better and faster. This makes them stronger in the global market.
- Creating jobs – Even though AI might replace some jobs, it also makes new ones. People will be needed to build, take care of, and oversee AI systems. Overall, there should be more jobs.
- Making more money – AI can help create new products and services. For example, it can predict what you might like to buy or suggest things you might need. This means more ways to make money.
- Making smarter choices – AI can help us make better decisions, whether it’s in business, healthcare, finance, or government.
- Saving money – By using AI, things can be done more efficiently, which means spending less money. This helps many types of businesses save cash.
- Growing the economy – When AI is used a lot, it can boost productivity, make people spend more, create jobs, and lead to more innovation. All of this helps the economy grow.
Cons of Using AI in Economies
Using AI in an economy can also bring some problems:
- Job losses – While AI creates new jobs, it can also take away some old ones, especially in areas like manufacturing, driving, and customer service.
- Shaking up businesses – AI can make some companies very successful, but others might struggle or even fail because they can’t keep up.
- Making inequality worse – Some people and businesses might make a lot of money from AI, while others lose out. This can make the gap between rich and poor even bigger.
- Cybersecurity issues – AI systems can have weaknesses that bad people can use to steal information, break privacy rules, or hack into things.
- Uncertainty – It’s hard to know for sure if AI will be good or bad for the economy. In some cases, the costs might be more than the benefits.
- Ethical worries – Without the right rules, AI systems could show favoritism, be unfair, break privacy rules, or cause problems we didn’t expect.
- Global tensions – Big countries like the U.S. and China are competing to be the best in AI. This competition could cause problems between them and change the balance of power in the world.
Comparative Analysis of AI Strategies among the Top Deca Economies
Here’s a complete comparison of the 10 countries discussed in the article:
| Country | Spending/Investment | Research Priorities | Applications | Ethics Guidelines | Key Initiatives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | – U.S. Government spending over $1 billion annually on unclassified AI R&D. – U.S. AI startups received $26.6 billion in VC funding in 2019. | – Machine learning, computer vision, natural language, robotics. – Heavily focused on defense, intelligence applications. | – Autonomous vehicles, precision medicine, algorithmic trading, smart cities, language processing. | – DOD adopts AI ethics principles. – Partnership on AI promotes best practices. | – American AI Initiative launched in 2019. – National AI Research Resource Task Force. |
| China | – Aims to reach parity with U.S. on AI research spending by 2025. – Planning $200 billion in AI-related funding by 2030. | – Computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing. – Strong focus on smart manufacturing and smart cities. | – Facial recognition, smart medical diagnosis, language translation, self-driving vehicles. | – Beijing AI Principles emphasize shared benefits. | – Next Generation AI Development Plan. – ‘New Generation’ national AI projects. |
| Japan | – Government spending $890 million on AI technology by 2025. – $4.6 billion public-private AI funding partnership launched in 2019. | – Manufacturing, healthcare, mobility, infrastructure, and disaster prevention. | – Robotics, autonomous driving, medical diagnosis, infrastructure management, image analysis. | – Society 5.0 initiative promotes human-centric AI. | – AI Technology Strategy. – Integrated Innovation Strategy 2020. |
| United Kingdom | – Government committed over $1 billion to AI sector deal. – Over $300 million in private AI investment in 2019. | – Healthcare, manufacturing, retail, finance, transportation, clean energy. | – Automated intelligence for cybersecurity, predictive analytics for finance, AI virtual assistants. | – Guidelines on ethics, transparency, privacy, accountability. | – AI Sector Deal to boost AI industry. – Office for AI created. |
| Canada | – Canadian Institute for Advanced Research received $125 million in AI funding. – Over $200 million invested into Montreal Institute for Learning Algorithms. | – Machine learning, deep learning, reinforcement learning. – Strong university research collaborations. | – Healthcare, natural resources, retail, financial services. | – Montreal Declaration outlines guiding principles. | – Pan-Canadian AI Strategy. – CIFAR AI Chairs program. |
| Germany | – German government will invest 3 billion euros in AI by 2025. | – Manufacturing, robotics, industry applications, logistics, supply chain. | – Autonomous machines for factories, embedded AI in manufactured products, smart logistics. | – Guidelines issued by Data Ethics Commission. | – National AI Strategy. – High-Tech Strategy 2025. |
| France | – Government pledged $1.6 billion for AI research over 4 years in 2018. | – Healthcare, autonomous transportation, defense, finance, agriculture, environment. | – Banking fraud detection, AI diagnosis tools, smart mobility, predictive analytics. | – Villani report provides ethical roadmap. | – National AI strategy with focus on research clusters. |
| Israel | – Government earmarked $250 million for AI tech initiatives by 2025. | – Machine learning, NLP, computer vision, convolutional neural nets, cybersecurity. | – Autonomous vehicles, precision agriculture, predictive analytics, personalized medicine. | – Israel Innovation Authority requires ethics review for grants. | – Israel Innovation Authority initiatives. – AI.GOV multi-year national program. |
| South Korea | – $2 billion public and private investment in AI by 2025. | – Machine learning, neural networks, robotics, computer vision. | – Smart factories, intelligent robots, autonomous vehicles, virtual assistants. | – AI R&D Guidelines recommend human-centric values. | – Mid- to Long-Term Master Plan in Preparation for the Intelligent Information Society. |
| Singapore | – Government committed $150 million to AI research in 2020. | – Fintech, transportation, healthcare, urban solutions, logistics. | – Chatbots for government services, risk management in finance, optimized port operations. | – AI Governance Framework guides responsible development. | – AI Singapore program. – National AI Strategy announced in 2019. |
FAQs
Yes, AI can make us more productive by doing boring tasks. According to one estimate, this might even double how fast our economies grow by 2035.
It’s a mix. There might be 58 million more jobs in 21 countries by 2030, but some jobs will disappear as well. We’ll need people to make, run, and watch over AI systems.
Think about jobs in transportation, manufacturing, retail, customer service, finance, medicine, and law. Jobs that involve simple, routine tasks might change the most.
This is a big worry. People with high-tech skills might get most of the benefits. Governments might have to make new rules and help people learn new skills to keep things fair.
They need to support research, make rules about things like privacy and competition, and balance making new things with making sure those things are safe and good for everyone.
The U.S. and China are trying really hard to be the best in AI. This could change who’s in charge in the world and make new kinds of problems.
Wrap It Up
AI presents vast potential and challenges for economies, demanding careful consideration and strategic planning to harness its benefits while mitigating risks. The coming decade is poised to witness profound transformations, making it crucial for nations to adapt and innovate in the AI landscape.
Read more related topics:
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.
More articles

Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.























































