Google Introduces Innovative Generative Image Dynamics That Simulate Dynamic Scenes in Static Images


Google has unveiled a Generative Image Dynamics, a novel approach enables the transformation of a single static image into a seamless looping video or an interactive dynamic scene, offering a wide array of practical applications.

At the core of this pioneering technology is the modeling of an image-space prior on scene dynamics. The objective is to create a comprehensive understanding of how objects and elements within an image may behave when subjected to various dynamic interactions. This understanding can then be used to simulate the response of object dynamics to user interactions effectively.
The key feature of this technology is the ability to generate seamless looping videos. By leveraging the image-space prior on scene dynamics, Google’s system can extrapolate and extend the motion of elements within an image, transforming it into a captivating and continuous video loop. This functionality opens up numerous creative possibilities for content creators and designers.
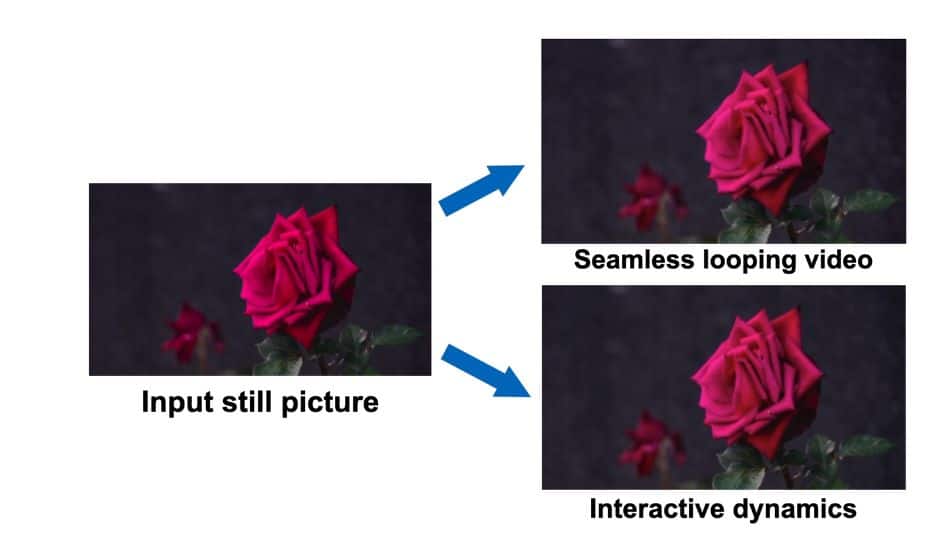
The technology enables users to interact with objects within static images realistically. By simulating the response of object dynamics to user excitation, Google’s system allows for immersive and interactive experiences within images. This has the potential to revolutionize metaverse spaces and how users engage with visual content.
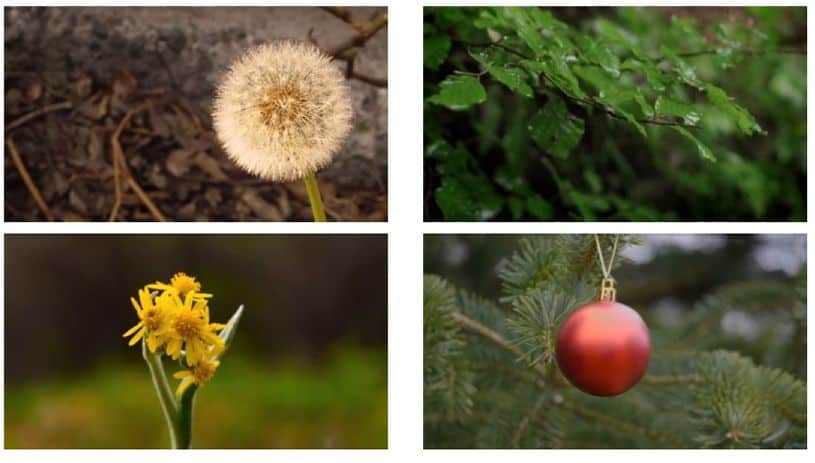

The foundation of this innovation lies in a meticulously trained model. Google’s model learns from a vast dataset of motion trajectories extracted from real video sequences featuring natural, oscillating motion. These sequences include scenes with elements like trees swaying, flowers moving, candles flickering, and clothes billowing in the wind. This diverse dataset enables the model to understand a broad range of dynamic behaviors.
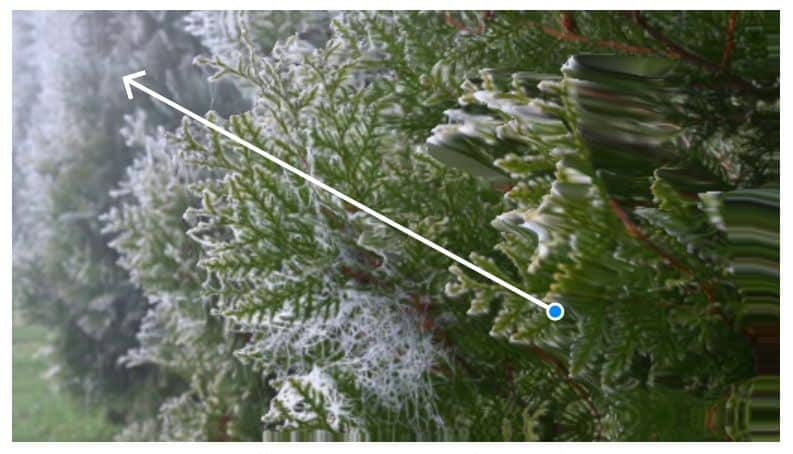

When presented with a single image, the trained model employs a frequency-coordinated diffusion sampling process. This process predicts a per-pixel long-term motion representation in the Fourier domain, termed a neural stochastic motion texture. This representation is then transformed into dense motion trajectories that span an entire video. Coupled with an image-based rendering module, these trajectories can be harnessed for various practical applications.
Compared with priors over raw RGB pixels, priors over motion capture more fundamental, lower-dimensional under-dimensional structure that efficiently explains variations in pixel values. This leads to more coherent long-term generation and more fine-grained control over animations compared to prior methods that perform image animation via raw video synthesis.
The generated motion representation is convenient for a number of downstream applications, such as creating seamless looping videos, editing the generated motion, and enabling interactive dynamic images, simulating the response of object dynamics to user-applied forces.
Read more related topics:
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.
More articles

Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.






















































